
Gr.Intl.Ch. Emir do Camping,
a descendent of Gr.Intl.Ch. Alferes do Camping, who got the award "Best
Head" given by the prestigious Brazilian judge and Fila breeder Wagner Bacconi.
Camping heads have been a trademark of Camping Kennel for 27 consecutive years.
Text by Clelia
Kruel. Sketches from the book O Grande Livro do Fila Brasileiro by
Procópio do Valle and Enio Monte.

#225 Official FCI Standard
translated by CBKC/FCI/SKC
judge Clelia Kruel to the English language
GENERAL APPEARANCE
Typically molossoid breed with powerful bones, rectangular and compact structure
but harmonious and proportional. Added to his massiveness a great agility can be
easily seen. Bitches must show a well-defined femininity which differentiates
them immediately from males.
CHARACTER AND TEMPERAMENT
Outstanding courage, determination, and bravery are part of his characteristics.
He is docile and obedient to his owners and family and extremely tolerant with
children. His faithfulness became a Brazilian proverb. He is always looking for
the company of his master. One of his characteristics is his "ojeriza" towards
strangers. He shows a calm disposition, self-assurance, and self-confidence, not
being disturbed by strange noises nor when facing a new environment. An
unsurpassed guardian of property, he is also inclined, by instinct, to hunt big
game and to herd cattle.
GAIT
The Fila has a long reach and elastic gait which reminds one of the great cats'
movements. His main characteristic is the pace (camel's gait), moving two legs
of one side first, followed by the two legs of the other side which causes a
rolling lateral movement of the thorax and hindquarters accentuated by the tail
when it is raised. During the walk he maintains the head lower than the back
line. He shows a smooth, free, and long reaching trot with a powerful stride.
His gallop is powerful with an unsuspected speed coming from such a large and
heavy dog. The Fila Brasileiro's gait is always influenced by its typically
molossoid articulations which give the impression, and in fact it is true, of
effectively permitting him sudden and swift changes in direction.
EXPRESSION
In repose it is a calm, noble, and full of self-assurance, never disclosing a
bored nor absent expression. When in attention, the expression should reflect
determination and alertness with a firm and piercing look in his eyes.
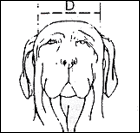
HEAD
The Fila's head is heavy and massive, always proportionate to the body. Seen
from above, it resembles a trapezoidal figure in which the head appears
pear-shaped. From a side view, muzzle and skull should have approximately the
proportion of one to one, or with the first being slightly smaller than the
second one.
SKULL
The profile shows a smooth curve from the stop to the occiput which is
well-defined and salient, especially in puppies. From a front view the skull is
wide, ample with the upper line slightly curved. The lateral lines descend
slightly curved, almost in a vertical line, narrowing toward the muzzle, never
showing a stop.
STOP
From a front view it is practically non-existent. The medium furrow runs up
smoothly until approximately the halfway mark of the skull. >From a side view
the stop is low, sloping, and virtually formed by the very well-developed
eyebrow ridges.
MUZZLE
Strong, broad, and deep, always in harmony with the skull. From a top view it is
full under the
eyes, very slightly narrowing toward the
middle of the muzzle and slightly broadening again until reaching the front
curve. From a side view the bridge of the muzzle is straight or has a Roman nose,
but never in an ascendant line. The front line of the muzzle is close to a
perpendicular line in relation to the superior line, showing a slight depression
right under the nose. A perfect curve is formed by the upper lips which are
thick and pendulous, drooping over the lower lips giving shape to the lower line
of the muzzle which is almost parallel to the upper line. The labial rim is
always apparent. The lower lips are close and firm up to the fangs and from
there on they are loose with dented borders. The muzzle has a great depth at the
root but without surpassing the length of the muzzle. The labial rim has the
shape of an inverted and deep U.
NOSE
Well-developed with broad nostrils not occupying entirely the maxilla width. The
color is black.
EYES
From medium to large size, almond-shaped, spaced well apart, from medium to
deep-set. The colors are from dark chestnut to yellow, always in harmony with
the coat color. Due to the profusion of the loose skin, many individuals present
drooping lower eyelids which are not considered a fault as such detail increases
the melancholic expression which is typical of the breed.
EARS
Pendant, large, thick, V-shaped, broad at the base and tapering at the end with
rounded tips. They are inserted at the posterior part of the skull in line with
the medium level of the eyes when in repose. When roused the ears go above the
original position. The root is oblique with the front border higher than the
back border. The ears are drooping at the cheeks or are folded back allowing the
interior to be seen.
TEETH
Noticeably wider than long. They are strong and white. The upper scissors are
broad at the root and sharp at the edges. Canines are powerful, well set and
well apart. A scissors bite is the ideal, but a level bite is acceptable.
NECK
Extraordinarily strong and well-muscled giving the impression of a short neck.
It is slightly curved on the top and well-detached from the skull. The throat is
furnished with dewlaps.
TOPLINE
The withers, standing in a sloping line, are set well apart from each other due
to the distance between the scapulas at a slightly lower level than the croup.
After the withers, the topline changes direction, ascending smoothly to the
croup, with no tendency to show a sway nor a roach back.
CROUP
Broad and long, with an approximate angulation of 30 degrees to the horizontal
line, showing a smooth curve. It stands a little higher than the withers. Viewed
from the rear the croup must be ample and its width is approximately equal to
the thorax and may be even wider in females.
BODY
Strong, broad, and deep, covered by thick and loose skin. The thorax is longer
than the abdomen. The length of the body is the same as the height at the
withers plus ten per cent, when measured from the point of the shoulder to the
point of the buttocks.
THORAX
The ribs are well sprung, though not interfering with the position of the
shoulders. The chest is deep and large, descending to the level of the elbows.
LOINS
Shorter and not as deep as the thorax, showing a separation of the two component
parts. The lower part of the loins is more developed in the females. Viewed from
above, the loins are narrower than the thorax and croup, but should not form a
waistline.
UNDERLINE
The chest is long and parallel to the ground in all its extension. The tuck-up
extends in a slightly ascending line but is never whippety.
FOREQUARTERS
The ideal shoulder structure should be composed of two bones of equal length (scapula
and humerus), with the former at an angle of 45 degrees from the horizontal line
and the humerus forming an approximate 90 degree angle with the scapula. The
articulation of the scapula-humerus forms the point of the shoulder which should
be situated at the level of the prosternum but a little behind it. In its ideal
position the shoulder covers the space from the withers to the prosternum and
the point of the shoulder should be placed halfway to this distance. An
imaginary perpendicular line coming down from the withers should cut the elbow
and reach the foot.
FORELEGS
Must be parallel, straight to the pasterns, and with powerful bones. The carpis
(pastern joints) are strong and apparent. The metacarpus (pasterns) are short
and slightly sloping. Length of the leg from ground to elbow should be equal to
the length from elbow to withers.
FEET
Formed by strong and well-arched toes which are not too close together. The pads
are thick, broad, and deep. The correct position of the feet is pointing to the
front. The nails are strong and dark, but they may be white when this is the
color of the respective toe.
HINDQUARTERS
The hindlegs are less heavy boned than the forelegs but never light as a whole.
The upper thigh has curved borders shaped by muscles descending from the ilium
and ischium, which trace the curve of the rear, and for this reason the ischium
must have a good length.
HINDLEGS
Parallel, with strong tarsis, metatarsis slightly bent, higher than the
metacarpis. The stifles and hocks are moderately angulated.
HINDFEET
A little more oval than the forefeet, but otherwise the description is identical
to that for the forefeet. They should not present dewclaws.
TAIL
Very wide at the root, medium set, reaching to the level of the hocks, tapering
rapidly at its end. When the dog is alert, the tail is raised high, and the
curve at the extremity is more accentuated. The tail should not fall over the
back or curl up.
HEIGHT
Measured at the withers:
Males: 65 to 75 cms. (25.5 inches to 29.5 inches)
Females: 60 to 70 cms. (23.5 inches to 27.5 inches)
WEIGHT
Males: minimum of 50 kgs. (l00 lbs.)
Females: minimum of 40 kgs. (90 lbs.)
COLOR
All solid colors are permitted except the disqualifying ones(white, mouse grey,
patched dogs, dappled, or black and tan). Brindles of a basic color, may have
the stripes of either less or with very strong intensity. A black mask may or
may not be present. In all permitted colors white markings should be limited to
the feet, chest, and tip of tail. The white markings are not desirable on any
other part of the body.
SKIN
One of the most important breed characteristics is the thick, loose skin over
the whole body, chiefly at the neck, forming pronounced dewlaps, and in many
individuals the folds proceed to the chest and abdomen. Some dogs show a fold at
the side of the head and also at the withers descending to the shoulder. When
the dog is in repose the head is free of wrinkles. When alert, in order to lift
the ears, the contraction of the skin at the skull forms little wrinkles along a
longitudinal line of the skull.
COAT
Short, smooth, dense and tight to the skin.
TEST OF TEMPERAMENT
This is compulsory requirement for all individuals (after 12 months) in order to
obtain a registered championship title.
All champions must have a certificate of
approval at the temperament test. This type of test is made at all specialty
shows. It is optional at general shows, up to the judge's will, providing it is
public and takes place outside of the show ring.
The trial includes:
Attack with a stick. The dog is supposed
to attack in front of the handler, without being coached, and the exhibitor or
handler will remain in his position. It is forbidden to touch or to beat the
animal.
Shooting test. There will be blanks fired
at a distance of five meters from the dog. The dog should express attention,
show self-confidence and self-assurance.
During all performances in the ring, the
judge will analyze the behavior and temperament of the entrant, paying attention
to his expression. During the temperament test the following should be observed:
Ģ The dislike of the animal to strangers.
Ģ The self-assurance, courage, determination, and braveness of each dog.
FAULTS
GENERAL FAULTS
Cryptorchid or monorchids, the use of artificial products, or a dog which has
been changed in appearance by artificial means, albinos, lack of typicity, etc.
DISQUALIFICATION
Aggressiveness toward his owner
Cowardice
Pink nose
Overshot bite
Undershot bite showing the teeth when the mouth is closed
Lack of one canine or one molar, other than the third one
Blue eyes (porcelain like)
Cropped ears or docked tail
Croup lower than the withers
All dogs that are white, mouse grey, patched, dappled or merle or black and tan
Under minimum height
Lack of loose skin
Lack of camel's pace
VERY SERIOUS FAULTS
Small head
Tight upper lips
A pronounced stop from a front view
Protruding eyes
Lack of two teeth except the PIS (first pre-molars)
Lack of dewlaps
Apathetic or timid dogs
Negative sensitivity to shooting a gun
Roach back
Level topline
Excessive tuckup
Cowhocks
Straight hocks (lack of angulation at the hindlegs)
Light bones
Lack of substance
Over maximum height
White markings exceeding l/4 of the body
Lack of pigmentation at eye rim
Round eyes
Square figure
SERIOUS FAULTS
Short muzzle
Small ears
High set ears (when in repose)
Excessively light colored eyes
Wrinkles on skull when the animal is in repose
Undershot bite
Lack of two teeth
Folded skin under throat that is not dewlap
Swayback
Narrow croup
A curled tail carried over the back
Chest lacking depth
Deviation of metacarpus or metatarsus
Over-angulated hindlegs
Short steps
MINOR FAULTS
Anything in disagreement with the standard that does not fall into the above
three categories
NOTE:
Male animals should have two apparently normal testicles fully descended into
the scrotum.